Biotech Could Benefit From Open Office Space
Written By: Colin A. Young
This article was originally published by The State House News on September 15, 2020.
SEPT. 15, 2020…..Commercial real estate and development experts said they are confident that the pandemic won’t spell the end of the development boom in and around Boston, but they said they are keeping their eyes on consumer and workforce trends that might reshape their industry.
During a virtual panel convened by NAOIP Massachusetts, the development pros said that while the COVID-19 pandemic slowed construction timelines and injected generous doses of uncertainty into the equation, development still has plenty of track in front of it in the Boston region.
“We operate between Boston and Washington, D.C., and I think that Boston is clearly the strongest market of those three and maybe the strongest market in the country,” Shawn Hurley, president of Marcus Partners said, referring to the Boston, New York City and Washington, D.C., markets. “It certainly seems that development in this market remains really strong and that our economy is more diversified than ever before. So we feel very good about the Boston market and how we’re positioned today, albeit in a very volatile world and as we enter what appears to be a potentially very volatile fall.”
Lauren O’Neil, senior managing director at JLL Capital Markets, said she doesn’t foresee a persistent slowdown in development in the Boston area. After desirable long-term investment-grade tenant leases, she said development appears to be second on the investment strategy depth chart.
“I think the thesis is that we may be in a bit of a slowdown now, but in two to three years when a project is set to deliver it sets up nicely for the rebound in this current slowdown, I won’t go as far as to call it a recession. And so we’ve seen investors and debt capital alike gravitating towards new developments,” O’Neil said. “And in fact, it’s probably easier right now to capitalize on new ground-up development than it is a value-add office deal, for example, where you might have 70 percent occupancy and you’re trying to get to 90 percent occupancy in the near term. There’s just more conviction on what the world will look like in a couple years versus over the next six months.”
O’Neil said hotels and retail developments are struggling to get financed right now. Retail developments with a grocer and that have “a compelling story” might fare better, she said.
“But with the delinquency rate on existing loans in the mid-teens for those product types, it’s going to be a bit of a challenge to get those C-Suites on board with making any sort of aggressive bets on retail and hotel for the foreseeable future,” she said.
Chris Brown, CEO of construction management firm John Moriarty & Associates, said biotech remains one of the hottest sectors in the marketplace right now and the “great need” for added research and lab space has not been diminished by the pandemic. At the same time, there’s “a little hesitancy” to commit to any deals involving traditional office space, given the uncertainties around the future of remote working and the return of most employees to the office.
“Biotech is probably the sector of the market that … will have the most traction moving forward,” he said.
Tamara Small, the CEO of NAIOP Massachusetts who moderated Tuesday’s discussion, asked Brown about converting office space to research or lab space, citing conversations she’s had with people who have suggested that “biotech is the new office.” Brown said his firm is working to “reposition” some office space at the Cambridgeside Galleria and has “a few other projects in the pipeline that look to take existing office space and potentially either add on to it or reposition it for biotech and lab space.”
“That seems to be one of the hottest sectors for us and the most interesting questions we get is in regards to that type of product as well,” he said.
O’Neil said converting office spaces to research or lab space for life sciences and biotech companies could help meet some of the demand for those spaces sooner than the pipeline of new construction could on its own.
“The demand from the tenants on the life science side was growing at an annual growth rate of a little over 8 percent and it’s projected to continue through 2023 at just over 7 percent, which if you look at the current 25.7 million square foot market, that means there’s demand for over 34 million square feet,” she said. “We’re about 3 million short of meeting that demand based on the current pipeline for 2023. Now, that generally includes only ground-up, brand new developments, so maybe the conversion factor will start to fill in some of that.”
The panel also took on the suburbs and the question of whether the pandemic, and the changes it has brought to commutes and daily life, is creating a time for the suburbs to shine and draw even more people out of urban cores. In July, real estate market analysts at the Warren Group said increases in sales in more rural parts of Massachusetts were “far in excess” of the state average.
“Cities are going to endure. The intrinsic qualities that brought everybody to them pre-COVID, we’re going to appreciate them all the more when this ends, and it will end. So we just envision a totally different kind of lifestyle returning when we’re through this,” Abe Menzin, a principal at the development firm Samuels & Associates, said. “In my more optimistic moments, I actually think that remote work options for people could actually enhance the vitality of cities. It could help shave the peaks off of some of the congestion issues that we’ve encountered, and could give people more flexibility in their lifestyle and make a livable city like Boston even more liveable.”
Kirk Sykes, a managing partner at Accordia Partners, is banking on people continuing to want to live in Boston but said aspects of two of his most significant projects aim to address concerns that the pandemic has highlighted. Sykes is involved in the plan to redevelop the site of the Boston State Hospital into a development with more than 360 housing units near Franklin Park and Mass. Audubon’s Boston Nature Center and Wildlife Sanctuary in Mattapan. He’s also part of the plan to convert the old Bayside Expo site in Dorchester into more than 1,000 units of housing, retail space, office space and more.
“We feel extremely blessed to have a 65-acre park, and the beach and the ocean in front of Bayside. And as such, I think those characteristics will play heavily into corporate relocations for campuses or even the decision to get on the train and go for five minutes to Kendall [Square] as opposed to being in Kendall,” he said. “So we’re designing in the desire to be in an environment that gives you the air, the light, the breath, the view that you might get in the suburbs, but getting it in a 20-minute bike ride, 30-minute walk or five-minute Uber/Lyft to the Financial District.”
-END-
09/15/2020











 The Coworking industry grew 50% between 2016 and 2018 and the variety of options within this market segment is staggering. Boston is no exception, currently, there are around 2.3 million square feet of coworking space in Boston and Cambridge. Last week
The Coworking industry grew 50% between 2016 and 2018 and the variety of options within this market segment is staggering. Boston is no exception, currently, there are around 2.3 million square feet of coworking space in Boston and Cambridge. Last week 
 Credit: Elisif Brandon
Credit: Elisif Brandon Courtesy of the MIT Center for Real Estate and Real Estate Innovation Lab –
Courtesy of the MIT Center for Real Estate and Real Estate Innovation Lab –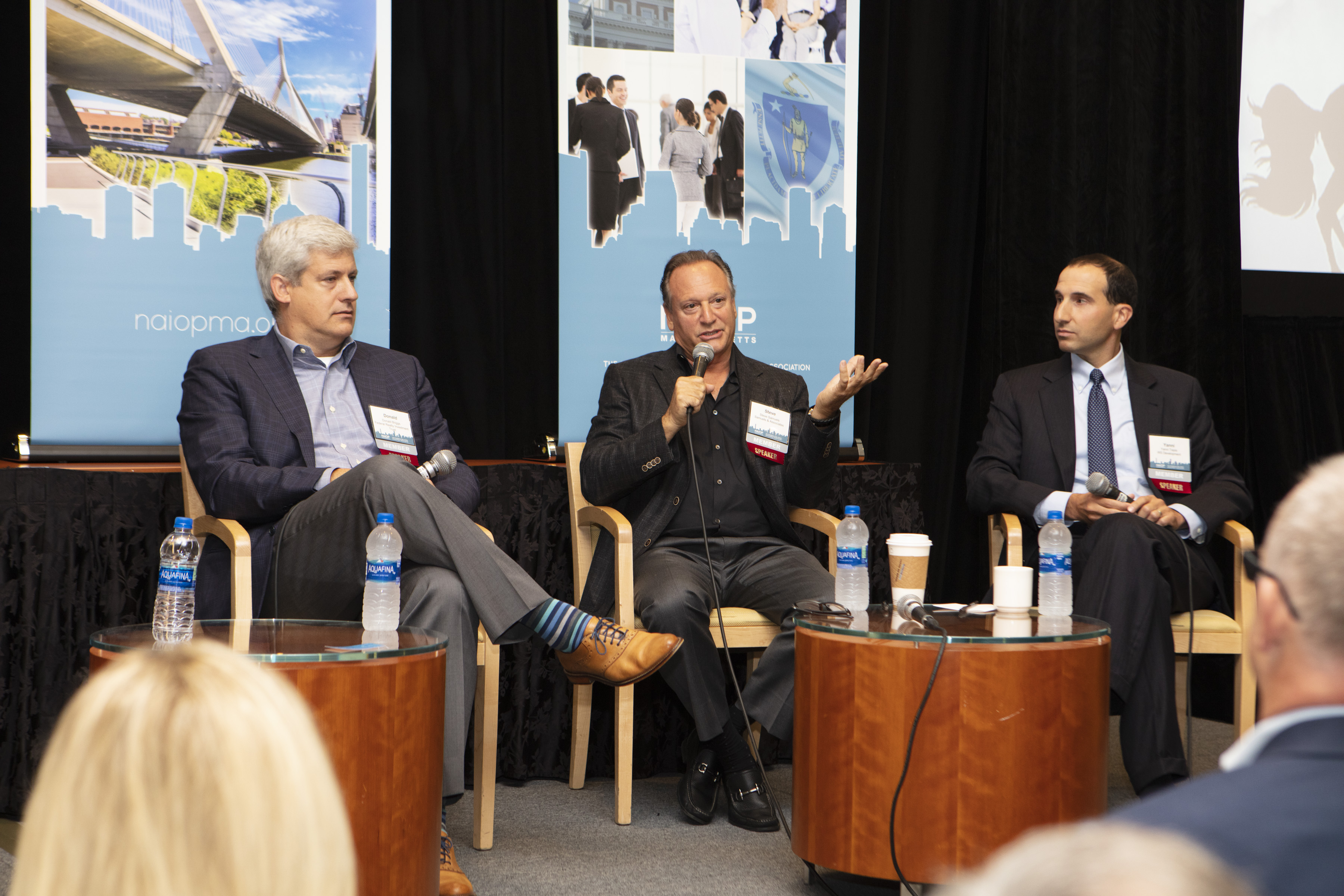  See
See  Fueled by one of the strongest economies in the nation, the Boston commercial real estate market should continue to thrive for the foreseeable future. That was the conclusion of the enthusiastic panel at the 2017 NAIOP/SIOR Annual Market Forecast held last week at the Westin Waterfront Hotel before a crowd of 450 CRE professionals.
Fueled by one of the strongest economies in the nation, the Boston commercial real estate market should continue to thrive for the foreseeable future. That was the conclusion of the enthusiastic panel at the 2017 NAIOP/SIOR Annual Market Forecast held last week at the Westin Waterfront Hotel before a crowd of 450 CRE professionals. But despite the positive outlook, there is a looming threat to the overall health of Greater Boston economy, he cautioned. “The housing stock is limited and growing too slowly to meet the demand, and as a result, home prices and rents continue to rise,” said Bluestone, who is one of the co-authors of the
But despite the positive outlook, there is a looming threat to the overall health of Greater Boston economy, he cautioned. “The housing stock is limited and growing too slowly to meet the demand, and as a result, home prices and rents continue to rise,” said Bluestone, who is one of the co-authors of the  JLL’s Heath led off the program with an overview of the Cambridge office and lab markets. “The Cambridge market is one of the strongest markets that we track globally at JLL, and it continues to be driven by this incredible demand from the tech and life science clusters,” she stated, adding that the demand is coming not only from organically grown companies, but outside firms seeking to establish an R&D presence in close proximity to
JLL’s Heath led off the program with an overview of the Cambridge office and lab markets. “The Cambridge market is one of the strongest markets that we track globally at JLL, and it continues to be driven by this incredible demand from the tech and life science clusters,” she stated, adding that the demand is coming not only from organically grown companies, but outside firms seeking to establish an R&D presence in close proximity to  Colliers’ Carroll reported that “the suburbs are alive and well”, as the market has added over five million SF of positive absorption since the downturn. There has also been a steady increase in rent growth in the Class A office market, approximately 10 percent since 2009, with new construction in Waltham achieving rents in the low $50s. The Class B market is not faring as well (although there is some rent growth occurring in select markets), with some of the older building stock being slated for repositioning or demolition to make way for senior living, hotel and other non-office uses (including 450,000 SF of properties in Chelmsford). One particularly bright spot is the emergence of biotech in the suburbs.
Colliers’ Carroll reported that “the suburbs are alive and well”, as the market has added over five million SF of positive absorption since the downturn. There has also been a steady increase in rent growth in the Class A office market, approximately 10 percent since 2009, with new construction in Waltham achieving rents in the low $50s. The Class B market is not faring as well (although there is some rent growth occurring in select markets), with some of the older building stock being slated for repositioning or demolition to make way for senior living, hotel and other non-office uses (including 450,000 SF of properties in Chelmsford). One particularly bright spot is the emergence of biotech in the suburbs.  Citing the enormous amount of commercial, residential, retail and restaurant development underway in the Seaport and other Boston locations, Avison Young’s Perry observed that “Boston is clearly a different city today than it was even five years ago.” The in-migration to the city by firms seeking talent continues, he said, citing the recent relocations by
Citing the enormous amount of commercial, residential, retail and restaurant development underway in the Seaport and other Boston locations, Avison Young’s Perry observed that “Boston is clearly a different city today than it was even five years ago.” The in-migration to the city by firms seeking talent continues, he said, citing the recent relocations by  NKF’s McDonald reported on the industrial market – the newfound darling of investors and developers – noting the transformational effect that Amazon and e-commerce has had on the product type. With 12.8 percent average annual returns to investors over the last five years, industrial has outperformed both retail (12.1) and multifamily (9.9), driven by feverish demand for “last mile” properties located in urban and infill submarkets. That demand has driven rents “way beyond the norms” of what had traditionally been $5 to $6 psf to the “high single digits and low teens” for buildings such as 480 Sprague St. in Dedham, a 234,000 SF warehouse that straddles the Boston line. And warehouse space located within the urban market, such as 202 Southampton St. in the South End (which lacks basics such as air-conditioning), is fetching $20 psf, based solely on location.
NKF’s McDonald reported on the industrial market – the newfound darling of investors and developers – noting the transformational effect that Amazon and e-commerce has had on the product type. With 12.8 percent average annual returns to investors over the last five years, industrial has outperformed both retail (12.1) and multifamily (9.9), driven by feverish demand for “last mile” properties located in urban and infill submarkets. That demand has driven rents “way beyond the norms” of what had traditionally been $5 to $6 psf to the “high single digits and low teens” for buildings such as 480 Sprague St. in Dedham, a 234,000 SF warehouse that straddles the Boston line. And warehouse space located within the urban market, such as 202 Southampton St. in the South End (which lacks basics such as air-conditioning), is fetching $20 psf, based solely on location. HFF’s Sayles addressed the ‘When will the cycle end?’ question early on his presentation. “End of cycle concerns have largely abated,” he reassured the gathering. “Nobody is really talking about that right now, instead, what people’s biggest concern is, ‘If I sell, what am I going to do with that capital?” He expects pricing for assets to remain flat in the near term with cap rates trending downward. Financing for assets is up by 17 percent from Q3 2016 to Q3 2017, but investment sales for that period declined by approximately 8.0 percent as buyers are choosing longer term holds. Sales volume for Boston is expected to be approximately $13 billion for 2017, with foreign capital again accounting for a significant portion of those transactions.
HFF’s Sayles addressed the ‘When will the cycle end?’ question early on his presentation. “End of cycle concerns have largely abated,” he reassured the gathering. “Nobody is really talking about that right now, instead, what people’s biggest concern is, ‘If I sell, what am I going to do with that capital?” He expects pricing for assets to remain flat in the near term with cap rates trending downward. Financing for assets is up by 17 percent from Q3 2016 to Q3 2017, but investment sales for that period declined by approximately 8.0 percent as buyers are choosing longer term holds. Sales volume for Boston is expected to be approximately $13 billion for 2017, with foreign capital again accounting for a significant portion of those transactions.